Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in the production of red blood cells, supporting the nervous system, and offering many health benefits. Despite its significance, many people may not get enough vitamin B12 from their diet, leading to a deficiency. This article will explore the various foods high in vitamin B12 and discuss the importance of maintaining appropriate levels of this nutrient in your body.
Primary Sources of Vitamin B12: Animal Products
Animal products are the primary sources of vitamin B12. These include red meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products. If you regularly eat meat, such as beef and lamb, you can easily meet your daily requirement for this vitamin. Organ meats like animal liver are particularly rich in vitamin B12, providing even more than muscle meats.
Fish, including cooked salmon, sardines, and mackerel, are excellent sources of vitamin B12. Some types of fish, like clams and mussels, have higher concentrations of vitamin B12 than any other food. In addition to being among the healthiest fish due to their lean protein content, they also contribute to heart health.
Dairy products like low-fat milk, cheese, and yogurt are good choices for B12 intake. They not only provide vitamin B12 but also other B vitamins, calcium, and protein. For those who prefer non-dairy milk, such as soy milk, these are often fortified with B12 and can be a viable option.
Plant-Based and Fortified Foods
For those who do not eat meat, several plant-based and fortified foods can provide vitamin B12. Nutritional yeast, a complete protein, is often fortified with B12 and other B vitamins. Non-dairy milks such as soy milk and almond milk are often fortified with this vitamin, making them good vegan sources of B12.
Fortified breakfast cereals and whole grains also contain B12. These fortified foods, along with a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, contribute to a varied and balanced diet.
The Role of Folic Acid and Other B Vitamins
Folic acid, another member of the B vitamin family, works closely with vitamin B12. It helps the body produce and maintain new cells, and it also prevents changes to DNA that may lead to cancer. Taking folic acid supplements can be beneficial, especially for pregnant women, to prevent neural tube defects in their babies. However, taking doses of too much folic acid can hide signs of vitamin B12 deficiency.
It's important to remember that all the folate in the world won't help if your body can't absorb it. Certain medications, like proton pump inhibitors for heartburn or Crohn's disease, can interfere with how your body absorbs these nutrients.
While all vitamins and minerals are essential to our health, B vitamins are involved in many body functions, especially brain and nerve functions. Here we will focus on folic acid and other important B vitamins and how they can benefit our health.
Folic Acid:
Folic acid is a B vitamin that plays an important role in the prevention of birth defects, such as spina bifida, and is critical during pregnancy. Besides its role in fetal development, folic acid is also critical for the production of DNA and red blood cells and helps prevent anemia. Folic acid is found in many green leafy vegetables such as spinach, broccoli, lentils, oranges, and beans.
Vitamin B6:
Vitamin B6 is a cofactor involved in over 100 essential enzymatic pathways in the body. It also helps to maintain healthy brain function, including serotonin and dopamine synthesis and regulating mood. Vitamin B6 helps the body create red blood cells and helps fight inflammation. Foods high in B6 include tuna, chicken, potatoes, bananas, and chickpeas.
Vitamin B12:
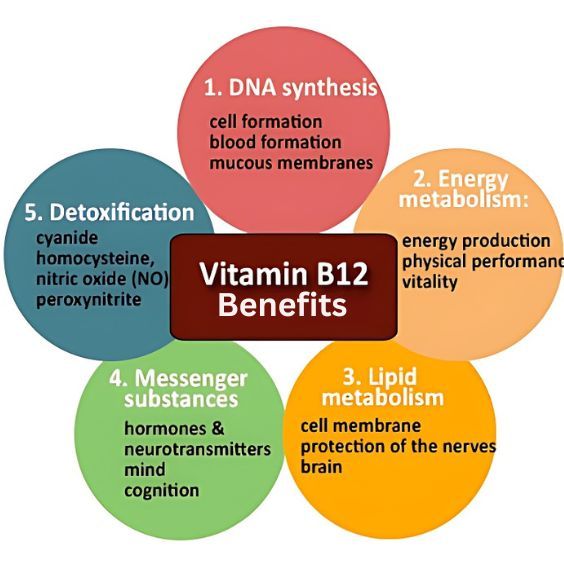
Vitamin B12 is essential for nervous system function, DNA synthesis, energy production, and the formation of red blood cells. It also plays a role in brain function, specifically, memory and thinking. Vegetarians and vegans may be at risk of a vitamin B12 deficiency because plants do not produce this critical nutrient. Vitamin B12 can be found in animal products like meat, fish, and dairy, or can be found in supplements.
Biotin:
Biotin is another essential B vitamin that helps the body convert food into energy, helps maintain healthy hair, skin, and nails, and supports fetal development. Supplements or biotin-rich foods can help with hair loss, brittle nails, and dry skin. Biotin is found in organ meats, eggs, and nuts.
Riboflavin:
Riboflavin helps to metabolize food and is necessary for cell growth and function. It is essential for healthy skin, eyes, and nerves. It’s also critical in the conversion of vitamin B6 to its active form. Large amounts of riboflavin are important for athletes and heavy exercisers since Riboflavin can help with recovery and endurance. Riboflavin can be found in milk, spinach, cheese, and almonds.
Fortified Foods: A Lifesaver for Vegans and Vegetarians
While animal product is the main sources of vitamin B12, there are also vegan sources available for those who do not consume animal products. These include fortified foods like fortified breakfast cereals and nutritional yeast. Fortified cereals are an easy way to get your B12, especially when combined with whole grains, which offer additional health benefits.
Dietary supplements are another option for those who may struggle to get enough vitamin B12 from their diet alone. This can include older adults, individuals with certain health conditions like Crohn's disease, or those taking proton pump inhibitors or heartburn medication, which can affect the body's ability to absorb B12.
Supplementation of Vitamin B12
For those at risk of deficiency, vitamin supplementation can be beneficial. Dietary supplements come in several forms, including tablets, capsules, and injections. They can help to maintain blood levels of vitamin B12 within the normal range.
High doses of vitamin B12 supplements are often recommended to treat pernicious anemia and vitamin B12 deficiency. Very high doses can also reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration, according to the National Institutes of Health.
However, it's important to note that while supplementation can prevent deficiency, it may not improve cognitive function in those without deficiency. A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found no difference in cognitive decline between a group given vitamin B12 supplements and a placebo group.
The Health Benefits of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is essential for human health. It helps the body produce red blood cells and supports the function of the nervous system. A deficiency in B12 can lead to pernicious anemia, a condition characterized by a lack of healthy red blood cells, leading to fatigue and weakness.
Furthermore, B12 works alongside other B vitamins, including folic acid, to maintain heart health. This combination has been shown to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. It is commonly recommended that pregnant women take folic acid supplements to help prevent neural tube defects in unborn babies. However, taking too much folic acid without a corresponding amount of B12 can mask a B12 deficiency and potentially lead to neurological problems.
On the other hand, maintaining an optimal level of B12 through a varied and balanced diet or supplements can provide many health benefits. Some studies suggest that adequate levels of B12 can reduce the risk of breast cancer and potentially lower all-cause mortality.


In conclusion, many foods are rich in vitamin B12, primarily animal products like meat, fish, and dairy. For those who do not consume animal products, fortified foods, and supplements can help meet their B12 needs. Ensuring an adequate intake of vitamin B12 is an important aspect of a healthy diet, contributing to the production of red blood cells, supporting the nervous system, and potentially offering protective effects against various health conditions.
So, whether you're a meat-eater, vegetarian, or vegan, with a little planning and knowledge, you can ensure you're getting enough of this key nutrient to stay healthy. For more personalized advice, consider consulting with health professionals who can guide you based on your specific needs and conditions.
Remember, a varied and balanced diet is the cornerstone of good health. By including foods high in vitamin B12 in your diet, you're taking an important step towards maintaining your overall well-being.